This article covers working with Application Storage to save app settings on app in xamarin forms App.
Introduction
Xamarin.Forms code runs on multiple platforms - each of which has its own filesystem. This means that reading and writing files are the most easily done tasks using native file APIs on each platform. Alternatively, embedded resources are also a simpler solution to distribute the data files with an app.
Application Storage
Xamarin Android - Shared Preferences
Android provides many ways of storing data of an application. One of this way is called Shared Preferences. Shared Preferences allow you to save and retrieve data in the form of key,value pair.
In order to use shared preferences, you have to call a method getSharedPreferences() that returns a SharedPreference instance pointing to the file that contains the values of preferences.
Xamarin iOS - NSUserDefaults
The NSUserDefaults class provides a way for iOS Apps and Extensions to programmatically interact with the system-wide Default System. By using the Defaults System, the user can configure an app's behavior or styling to meet their preferences (based on the design of the app). For example, to present data in Metric vs Imperial measurements or select a given UI Theme.
UWP - ApplicationDataContainer
Represents a container for app settings. The methods and properties of this class support creating, deleting, enumerating, and traversing the container hierarchy.
Xamarin Forms - Properties Dictionary
The Application subclass has a static Properties dictionary which can be used to store data, in particular for use in the OnStart, OnSleep, and OnResume methods. This can be accessed from anywhere in your Xamarin.Forms code using Application.Current.Properties.
The Properties dictionary uses a string key and stores an object value.
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 2017(Windows or Mac)
Start by creating a new Xamarin.Forms project. You’ll learn more by going through the steps yourself.
Choose the Cross-platform App project under Visual C#-->Cross-platform in the New Project dialog.
Now Select the Blank App and Choose Portable Class Library(PCL).
You now have a basic Xamarin.Forms app. Click the Play button to try it out.
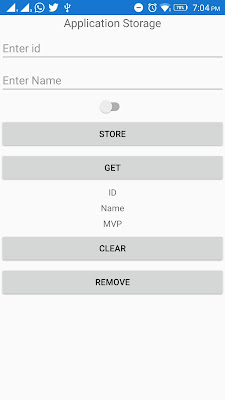
Setting up the User Interface.
Go to MainPage.Xaml and write the following code.
MainPage.Xaml
Store Value
The Properties dictionary uses a string key and stores an object value.
Now, write the following code on BtnStore_Clicked event.
MainPage.Xaml.cs
Get Value
The Properties dictionary stores objects so you need to cast its value before using it.
Now, write the following code on BtnGet_Clicked event.
MainPage.Xaml.cs
Remove Value
If you want to remove values, you can remove it.
Now, write the following code on BtnRemove_Clicked event.
MainPage.Xaml.cs
Clear Values
If you want clear all Properties.you can following code.
Now, write the following code on BtnClear_Clicked event.
MainPage.Xaml.cs
Full Code
MainPage.Xaml.cs
Click the Play button to try it out.
I hope you have understood how to use Application Storage in Xamarin forms
Thanks for reading. Please share comments and feedback.

















Thanks for sharing this informative content , Great work
ReplyDeleteLeanpitch provides online training in ICP CAT during this lockdown period everyone can use it wisely.
ICP-CAT certification